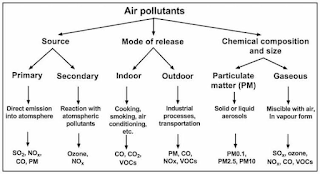
Q.1 Define air pollution air pollution and also classify the air pollutants according to their origin.
(B) Give classification of air pollutants according to state of matter with appreciate example.
(c) Explain in detail the effects of carbon monoxide on human health in detail.
- Mild headache
- shortness of breath
- chest pain
- weakness
- Losses of muscle
- mental confusion
- upset stomach
- vomiting
Q.2
(A). Enlist different types of fuels used in vehicle also unlist air pollutants emitted by each type of fuel.
| Fuels |
Air pollutants |
| Petrol | CO, NOx, PM, Unburn Hydrocarbon |
| Diesel | volatile organic compounds and NOx. |
| CNG | CH4 as slip and CO & HCHO gas. |
| Bio-diesel | PM, CO, HC |
| Ethanol | Ground Level Ozone |
| Electricity | Green House Gases |
(B) A sample of analyse at 0°c and 1 ATM pressure is reported to content 9 PPM of carbon monoxide (CO) determine the equivalent carbon monoxide (CO) concentration in microorganism per cubic metre and milligram per cubic metre.
Explanation : The Equivalent concentration in milligram per cubic metre is 11.25 mg/m.
1PPM : 1.250 mg/m.
So, 9PPM = 9 * 1.250 = 11.25 mg/m.
So the correct answer is 11.25 milligram per metre are analysed 80 degree Celsius and 1 ATM pressure is reported to contain 9 PPM of carbon monoxide the equivalent carbon monoxide concentration milligram per metre is 11.25 mg/m.
(C) write a detail note on "procedure for stake gas sampling"
Stake sampling also sampling may be defined as the method of collecting representative sample of pollutant at the place of audition of pollutants to determine the total amount of pollutant ameted into the atmosphere from a given source in a given time.
Source sampling is usually carried out in a process to determine the emission rate or characteristic of pollutants.
Planing : the success of state sampling depends on proper initial planning the planning include following.
- Method of sampling.
- Method of analysis sample.
- Sampling time because certain Industries undergo cyclic change.
- Amount of sample Required.
- Sample Frequency.
It is highly important that the sample collected most of truely represent the condition prevent inside the stack.
1. Accurate measurement of pressure, moisture, humidity and gas composition.
2. The selection of suitable location for sampling.
3. Determine the point required for velocity and temperature profile across the cross section of stick and sampling for particular matter.
4. Measurement of this rate of flow of gas or air through the stack.
5. Selection of a suitable sampling train.
6. Accurate isocratic sampling rate is especially for particulate sampling.
7. Accurate measurement of weight and volume of sample collected.
(C) state the use of high volume sampling and explain its working.
High volume at sampler are the basic instrument used in monitoring of ambient air quality.
It's work on stocks low for collection of particulate.

.jpg)

0 Comments