COD ( waste water quality parameter )
COD : chemical oxygen demand
➙ COD ( chemical oxygen demand ) indicate how much organic pollutants is present.
| • BOD • COD | Used for organic pollutants strength |
Definition COD :
➙ Chemical oxygen demand is the test to determine the amount of oxygen required to oxidized organic matter in acid condition into carbon dioxide ( CO2) and water ( H2O ) using strong oxidizing agent.
Limitation of Chemical Oxygen Demand Test
➙ No clarification of biodegradable and non biodegradable organic compounds present in sample.
- COD = BOD + Non Biodegradable
- COD - BOD = Non Biodegradable
➙ All The Organic Matters Does Not Oxidize With Weight Chemicals Method.
Example: aromatic hydrocarbons ( phenol )
➙ When the best water have presence of inorganic compound like, chlorine, sulfate etc. Then auto is consume by this organic compounds and COD results will be errornevs.
➙it does not provide any information about the rate at which organic compounds are being stabilize/oxidise.
Advantage of chemical oxygen demand ( COD )
➙Short analysis time compared to BOD Test.
| BOD Test | 3 or 5 day's |
| COD Test | 3 hours |
➙ Sometime COD test can be perform when COD and BOD ratio are Established.
History of COD Test
➙By oxidizing agent = K2 Cr2 O7 ( Potasium Dichromate )
➙KMno4 ( potassium permanent )
➙K2Cr2O7 :- Available in High scale of purity ( 99.9% purity).
➙K2Cr2O7 is a primary solution and price is cheap as compare KMno4.
➙K2Cr2O7 more strong oxidizing agent.
Limitation :
- Low molecular Fatty acid
- Pyridine - non biodegradable
- Aromatic hydrocarbons
➙Compound | chemical used to remove interface
Note :
➙Theoretical Oxygen Demand is High > COD > BOD
Chemical Oxygen Demand :
➙COD in mg/L = O2 consumed ( strong oxidizing agent )
➙K2Cr2O7 ( how ml of K2Cr2O7 used )
➙Strength of oxidizing agent ( K2Cr2O7 )
- 1ml 1N of K2Cr2O7 = 8 mg of O2
- 1ml , N/8 K2Cr2O7 = 1 mg of O2
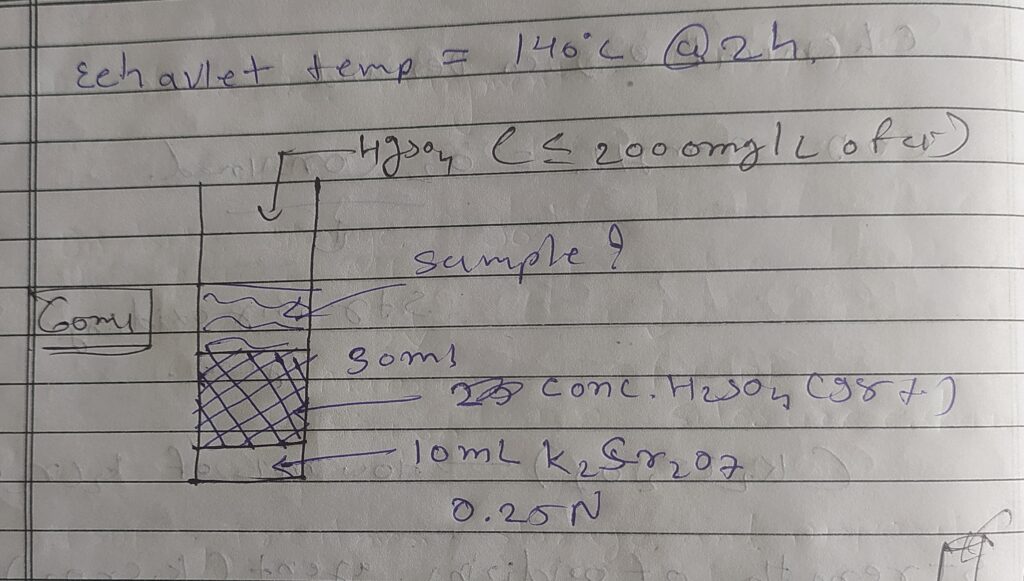
➙Acidic condition - concentration H2SO4
➙Chlorides ( Cl-) > Hgso4, nitrites ( No2-) > sulfamic acids
➙Elevate temperature : 140°c @ 2h
➙Note : COD concentration < 8000 mg/l
➙There are Two Types of COD Determination :
- Direct COD determination ( COD < 800 mg/l )
- Dilation method ( COD > 800 mg/l )
| COD Unit is | mg/l |


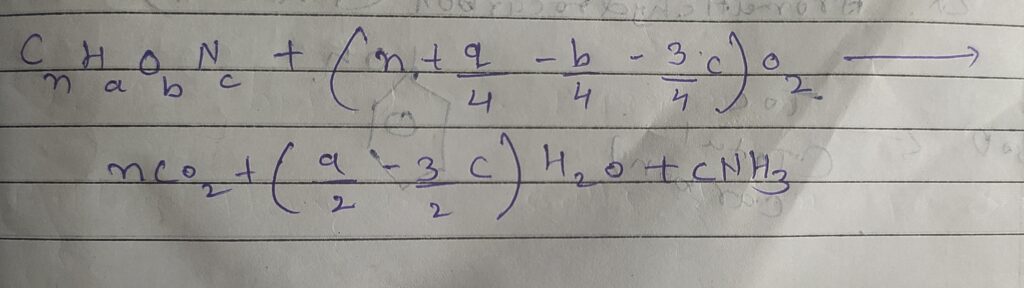
.jpg)

0 Comments