1. Define The Following Terms.
• Sedimentation : sedimentation is the process of separation of suspended particles that are heavier than water and from water and wastewater under action of gravity due to their weight or specific gravity.
➙ sedimentation is unit operation.
➙ The term sedimentation, settling and classification are used interchangeably.
➙ The Sedimentation Basin me also we know as,
• Discrete Particles : Particles whose size, shape and specific gravity do not change time and Depth of sedimentation Tank are know as discrete particles.
• Flocculant Particle : particle whose surface property are such as the aggregate with other particles due to contact and size shape and specific gravity change with each contact are called Flocculating particles.
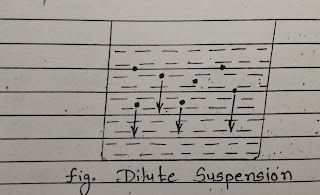
• Dilute Concentration : Suspension in which the concentration of particle is not sufficient to cause inter particle forces as they settle.
Particle concentration is very low and particles are not close enough to cause velocity field interference.
Dilute suspension are most common encounter in water treatment.
• Concentrated Suspension : Suspension is which the concentration of particle is too great to cause considerable inter particle force.
Due to a High Particle concentration, During Settling they interference the velocity part of other particles.
Concentrated suspension are most commonly encountered in waste water treatment.
2. Explain The concept of Sedimentation for Wastewater Treatment and Write The Application of Sedimentation in water Treatment and wastewater Treatment.
Concept of sedimentation :
When liquid containing solid in suspension in placed in a relatively quiescent State. those solids having Higher Specific gravity then liquid will tend to settle and those with a lower specific gravity will float on surface of liquid.
The Objective of Treatment by Sedimentation :
- To Remove Radially Settable level solids.
- To Remove Suspended solids.
- To Remove Floating matter.
Application of Sedimentation :
- Grid removal in Grid chamber.
- Particular matter remove in primary. sedimentation tank.
- Biological flocks remove in activated sludge process.
- Chemical flocs remove when's chemicals are used.
- Solid concentration in such thickening facility.
- Free oil and floating matter removal.
- To provide sufficient detention time for effective chlorination.
- Also, used for storm water retention time to remove measured portion of organic solids.
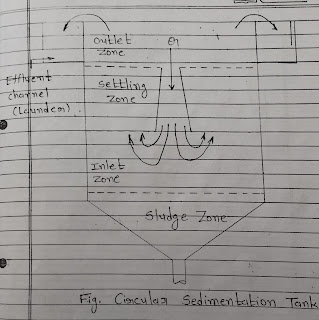
3. Draw The Line Sketch and Indicate Different Zone of Sedimentation in :
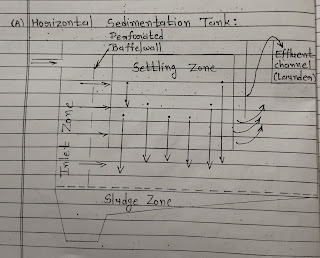
(A) Horizontal Sedimentation Tank :
4. Explain following zones of sedimentation tank with figure.
- Inlet zone.
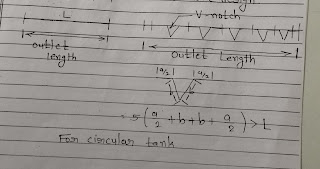
- Settling zone.
- Outlet zone.
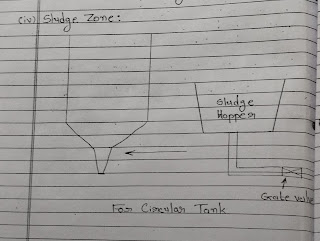
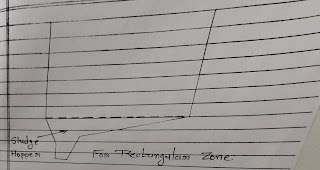
- Sludge zone.
1. Inlet zone :
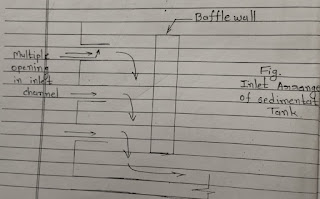
The inlet zone should be design in such way, that incoming water in Uniformly Distributed in the full width of tank and enter The sedimentation zone without causing any disturbing particle.
It consists of series of inlet pipes or Baffle Walls extending about 1 m into the tank reduce incoming water velocity.
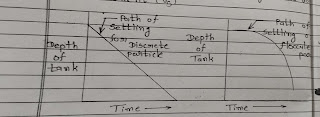
2. Settling Zone/Sedimentation Zone :
The condition for entering the particle in settling zone is,
L/Vo> H/Vs
Where,
- H = Depth of settling zone.
- L = Length of settling zone.
- Vo = Horizontal Velocity of Flow of water.
- Vs = settling velocity of particle.
- The Horizontal Force of water, gives the horizontal moment ( Vo )
- The Gravitational force of particle give it downward moment (Vs)
Cast iron pipes with gate valves are provided at lowest point of the floor.
Generally Sludge Hopper is design with side Sloping with a vertical to horizontal ratio of 1.2 :1 to 2:1 ( for circular tank and 8% slope tonver one side for Rectangular Tank )





.jpg)

0 Comments