1. Define the following terms :
• Global Navigation satellite system (GNSS) :
Global Navigation satellite system referred to a constellation of satellite provides signal from space that Transmit position and timing data to (GNSS) receiver.
The Receiver then use this data to determined location by definition, GNSS provides Global coverage.
Example of GNSS including Europe's Galileo, The USA's NAVSTAR Global Position System (GPS), Rassia's Global Naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnik vaya Sistema ( GLONASS ).
The performance of GNSS is assign using 4 criteria :
- GPS :
The Global positioning system (GPS) is US own utility that provide users with positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) services.
The system consists of 3 segment :
- Space segment
- Control segment
- User segment
The US space Force Develops, maintain and operates the space and control segment.
- Timing and Ranging :
The distance from a given satellite objects occurs The velocity of Transmitted signal Multiplied by The time taken by the signal to reach us.
Velocity * Travel Time = Distance
The ranging is referred as a 'Pseudo-range'.
- Satellite Clock ERROR :
The satellite clock error is caused by the satellite oscillation not being synchronized today GPS time and it is one of the main error which affect position accuracy.
The Broadcast Navigation message provide the clock Error as the coefficient of poly nominal and is updated every 2 hours.
- Atomic clock :
Atomic clock Types of clock that uses certain regional frequencies of atoms to keep time with Extreme accuracy.
The Electronic Components of Atomic clock are Regulated by the Frequency of Microwave Electro-magnetic Radiation.
Only when this radiation is maintain at a high specific frequency will it induce energy change of the cesium or rubidium.
In an Atomic Clock is Quantum Transition Observe and Maintenance in a Feedback loop That Frequency of the Electromagnetic Radiation.
- GPS P CODE :
The P code is called the Precise Code.
It is the particular series of once and zeros generated at a rate of 10.23 million bits per second.
This assignment of the particular week of the 27 week long P CODE it satellite help a GPS receive distinguish one satellite transmission from another.
- Triangulation & Trilaterations.
A Global Position System GPS device use data from satellite to locate a specific point of the earth in process called Triangulation.
To Tritaterate,a GPS receiver measure the distance to satellite using radio signals.
Trilaterations is the similar to triangu*s = satellite location which measure angle depicted L = location in this illustration.
- Almanac :
Containing less accurate orbital information than Ephemerides.
Valid for a period of up to 90 days.
Used to speed up time to first fixed by 15 seconds.
Those the receiver is capable of computing a position without having an Almanac present.
The Almanac herbs out with fixed the satellite for the first time but that is about it.
- Ephemerides :
It contain information on which number satellite accuracy & health age of data, satellite clock correction, coefficient, Orbit parameter.
Valid it 2 hours before and 2 hours after time of Ephemerides.
The Ephemerides can be through of as when data was completed from GNSS control segment.
Used from Real Time Satellite coordinate completed which is required in position computation.
- Ground Truth:
Ground Truth of Satellite image means the Collection of information at particular location.
It's allow satellite image data to be deleted to real feature and materials on the ground.
This information is frequently used for calibration of Remote sensing data and compared the result with Ground Truth.
Ground truth data artificial collected by visit a site & perform some experiment like survey on that particular location, measuring difference properties and features of location like area coverage by forest, agriculture, water, Buildings and other class of lands by performing surface observation in different aspect.
- Sea Truth :
Sea Truth is define the observation and collection of information about the actual condition in sea.
2. Enlist and describe functional segment of GPS.
- Space segment
- Control Segment
- User Segment
1. Space segment :
GPS satellite fly in circular orbit at an altitude of 20,200 km & with a period of 12 hours powered by solar cells.
The satellite continuously Orbit themselves 2 point there solar panels turnover the sun and their antenna townrd to the earth.
Orbital planner are centred on the earth.
Orbits are designed so that at least, 6 satellite are always within line of sight from any location on the planet.
- Control Segment :
The control segment consist of worldwide monitor and control station that maintain the satellite in their proper Orbit through occasional command measurement and adjust the satellite clock.
It Track the GPS satellite, upload updated navigation data and maintenance health and status of the satellite constellation.
The control segment consists of 3 Entities:
(1). Master Control Station :
The Master Control Station Located at Falcon air force based in colarado springs.
It is responsible for overall management of the remote monitoring and transmission sites.
Check-up is Perform Twice a day by each of 6 stations as the satellite completed their journey around the earth.
Can preposition satellite to maintain and optimal GPS constellation.
(2). Monitor stations :
Checks the extra altitude position speed and overall health of the orbit satellites.
The control segment ensure that dgps satellite orbit and clocks remain within acceptable limits.
Station can track up to 11 satellites at the time.
This check up is perform twice a day, by each station.
(3). Ground antennas :
Ground antina's monitor and tractor satellites from horizon to Horizon.
They also transmit correction information to individual satellites.
Communicate with dgps satellite from common and control purpose.
3. User Segment :
GPS receiver a generally composed of,
- An antenna ( turn to the frequency an by the satellite )
- Receiver - Processor
- Highly stable clock commonly crystal oscillator.
They can also include a display for sovin location and speed information to the users.
Receiver is often describe by its number channels.
As of recent receiver usually have between and 20 channels.
3. Define : Ground Truth Data and Discuss the Requirement of Ground Truth Data.
Ground floor is a term used in a range of remote sensing techniques.
It is generally referred to the data collected 'onside' on surface of the earth regarding characteristic of the Earth surface features.
Ground Truth Data are complementary to the Remote Sensing data as it helps to link the image data to ground reality.
The Ground Truth Data is not always true as it may have error in it due to factor such as :
- Error introduce during data collection.
- Data processing.
- Deriving inference from them.
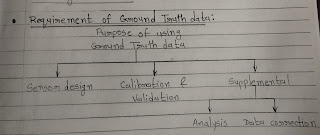
Requirement Of Ground Truth Data :
The purpose of acquiring brown truth is ultimately to aid in calibrating and interpreting remotely recorded imaginary by checking ground reality's within the scene.
Since human interruption normally experience the earth a ground dwellers ; there view of the world from a horizontal or low ; angel Panorama the customary frame of reference.
Generally, ground data should be collected at the same time as data acquisition by the remote sensor or at least within the time that Environment condition does not change.
It should not be interference that the use of the word "truth" implies that ground truth data without error.
Ground data is used for sensor design calibration and validation as well as supplemental use.
Calibration and validation involves calibration of sensor as well as the captured data calibrated of sensor is perform to obtain a standard desired Reflectance in the output image for a given material.
Calibration of data is perform to match the pixel value to the original reflection of the object and validation the data for analysis.
For supplement purpose those are two application namely, analysis and data correction.
The item to be investigate by ground data are as follow :
- Information about the object Type, Status, special characteristic, circumstances, surface temperature etc.
- Information about the environmental the sun and elevation irracdiance of the Sun atmosphere elarity, temperature, humidity, wind direction, wind velocity, ground surface condition etc.
4. Enlist and Explain The affecting parameter of Ground Truthing.
(A) Atmospheric Condition :
Ground Truth Data are used to correct the image for condition in the atmosphere that intercept incoming solar radiation, there by affecting the intensity or frequency of reflected energy signal.
The surface water and vegetation special data should be collected at the imaging time, + and - a few hours.
The atmospheric condition of interest are :
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Wind Direction and speed
- Sun elevation and azimuth
- Maze or Aerosol.
(B) surface water :
In place where surface water bodies are of surface and size and interest.
Ground data should be collected to represent each type of water condition.
Clean water absorb most of solar radiation reflectively increase with tea presence of solid organic or inorganic and the presence of certain dissolve species can also after the apparents on the image.
(C) vegetation :
Presuming that the analysis of interest is that of vegetative health, species composition or plant community mapping, spectral measurements of the various vegetation types in the field with be required.
For example for 5m * 5m pixels the spectrals response for a stand of vegetation consist of a combination of the spectra of all vegetation type and the soil ground liter etc. within the picture element.
(D) Soil, Bare Ground & Rocks:
The data collection for soil measurements, as in vegetation spectral sampling should strive to represented the various types of soil or contaminate condition.
Moist soil are darker & therefore at sides where content varies it is a good idea to measure both wet and dry soil condition.
(E) dark and light calibration targets :
Acquiring spectral measurement uniform bright dark calibration target area within site remind the minimum size of this target area should the pixel resolution of the image instrument.
Preferable size equal to 9 to 25 pixel or more.
This Target area should be on flood ground homogeneous and as close as possible targets the can be used are Asphalt, cement sand and flat aluminium roofs or bare dirt areas.
The Reflectors of this dark and light targets their no spectral response are used to the image and the correct for Atmospheric influence.
6. Explain the ERROR introduce in GPS.
- Satellite Error
- Satellite Orbits
- Multipath Error
- Atmospheric path
- Receiver Error
- Selectively Availability
- Satellite Error :
Slight inaccuracies in time keeping by the satellite can cause error in calculating position.
Satellite drift slightly from there predic Orbit which contributes the error.
- Satellite orbits :
Sun and moon have a week influence on the orbit the resulting error being not more than 2m.
- Multi Path Errors:
As GPS signal finally arrive at the Earth surface it may be reflected by local obstruction before it gets to the receivers antenna.
This is multipath error as the signal is reaching the antenna is single line path as well as delayed Path.
The effect is similar to a double image on a TV set.
The multipath error is caused by reflection of satellite signals on orbits.
For GPS signals this effects mainly appears in neighbourhood of large building or other elevation.
The reflected signals take more time to reach receiver than the direct signal.
The resulting error typically Lies in the range of few metres.
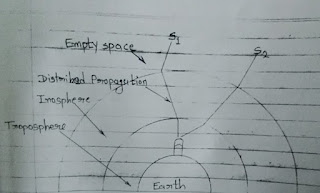
- Atmospheric Effect :
The GPS signals have to travel through change particles and water vapour in the atmosphere which delay it's transmission.
Since the atmosphere various at different place at different times, it is not possible to accurate compensate for the delay occurs.
While the radio signal struggle the velocity of light the outer space, there propagation in the ions and troposphere is slower.
Ionosphere in a height of 80 to 400 km a large number of e- and + charged ions are formed by the ionizing for the sun.
The larger reflected the electromagnetic waves from the satellites resulting in an elongated runtime of the signals.
Since the electromagnetic waves EMIT in form of a sphere therefore inverse square Law is employed and the square of their frequency while passing the inosphere.
The reason for reflection in troposphere are different concentration of water vapour caused by different weather condition.
The error cost that way is smaller than the ionosphere error but cannot be eliminate by calculation.
In an only approximately by a General calculation model.
- Receiver Error :
Since the receiver are also not perfect they can introduce their own error which usually occur from their clocks or internal noise.
Despite the synchronization of the receiver clock with the satellite time during the position determination the remaining in in accuracy of the time still lid to an error of about 2 m in the position of determination.
Rounding and calculating error of the receiver sum of approximately of 1 m.
- Selective Availability :
Selective availability was the international error introduced by DOD to make sure that no hostile force used to accuracy of GPS against the US or its Allies.
On May 1st 2000, the White House announce decision to discontinue the international degradation of GPS signal to the public.
Civilian users of GPS will be able to pin point location up to 10 times more accurately.
7. Discuss the working principle of DGPS.
The working of the Global Position System based on the 'trilateration' mathematical principle.
The position is determined from the distance measurement to satellite.
The force satellite are used to determine the position of the receiver on the earth.
The target location is confirm by the fourth satellite and third satellite are used to treace the location place.
A 4th satellite is used to confirm the target location of each of those space vehicles.
The GPS consist of satellite, control station, monitor station and receiver.
The GPS receiver takes the information from the satellite and users the method of triangulation to determine a user extra position.
8. Discuss the basic principle of calculating location by GPS receiver.
The basic of GPS is 'Triangulation' from satellite.
The Triangulation is the GPS receiver measurement distance using the travel time of radio signals.
To measurement travel time GPS needs very accurate timing along with distance when it took no exactly where the satellite are in this space.
Suppose we measure our distance to the second satellite and find out that it is 21000 km away.
This convince that we are not only the first but we are also on the that is 21000 km from the second satellite.
If we make measurement from third satellite and find that we are 22000 km away.
This convince that we can narrow our position to just 2 points in space.
The points different greatly in latitude/ longidute, position and altitude.
So by addition 4th satellite receiver can be determine out 3rd position.
Every GPS receiver is essentially and atomic clock.
Receiver cloth should be perfect so that all satellite range would intersect at a signal point.
It is necessary for all detect GPS receiver 2 Aqua at least four channel so that it can make 4 measurement simultaneously.
The receiver must be solved for its position and clock time using following equation ,
9. Define time synchronization how can be achieve time synchronization.
synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison.
GPS satellite include 3 to 4 atomic clock that are monitor and control to be high synchronized and traceable to National and international standards.
So for time synchronization, the GPS signals is received, process by a local master clock, time or primary reference and Passed on the other device systems or network so there local clock are linked wise synchronized to UTC.
Typical accuracy range from better than 1ms to a few milliseconds depend on the synchronization.
It is the process of synchronization GPS that can provide atomic clock accurately without the need for a local atomic clock.
In any case GPS clock synchronization eliminates the need for manual clock settling to established
Traceability to National and international standards.
So various events can be correlated even when they are time stamped by different clocks.



.jpg)

0 Comments