Potentiometry
1. Explain The Teams :
(A) potentiometry :
→ In chemical analysis, potentiometry is method in which the potential between two electrode is measured while the electric current between the electrodes is controlled.
→ It is measurement of electric ometer.
→The potential of one electrode known as the working or indicatos electrode f gesponds to analyte's activity. The other electrode on reference electrode has known fixed potential.
(B) Polarography :
→ The planography is an electrochemical method of analysis based on the measurement of cument flow resulting from the electrolysis of the solution at a polandsable micro-electrode as a function of applied voltage.
→ Polanography is based pion principle that gradually increasing voltage is applied between 2 electrodes. 1 of which is polarisable ( droping Mercury electrode ) and other is non polarisable electrode f current flowing between 2 Electrode is reconded.
→ Diffusion current is used for determination of concentration of substance.
(c) Diffusion Current:
→It arises due to the migration of analyte species from the bulk of solution. towards mico electrode and it's magnitude is depends on law of diffusion.
→Current caused by diffusion of Depolarization potential enables identification of ion's present in soln & by measuring diffusion current their conc. in is calculated.
(d) Define: pH
→ pH is measure of H+ ions present in any solution.
→ It tells you how acidic your solution is.
→ Importance Of Ph In Environmental Field:
- Disinfection
- corrosion control
- chemical coagulation.
- sludge Dewatering
- Microorganism in biological Treatment.
2. Explain the following instrument :
(1) Potentiometer :
→ The principle of a Potentiometer is that the potential dropped across a segment of wire of uniform crogs section carrying a constant current is directly proportional to its length.
→ The potention meter is simple device used to measure the electric potential.
(2) Ion- selective Meter :
→ Ion - selective meters maybe configured to measure one of several different types of ion, depending on the electrode used.
- A sensing electrode
- A reference electrode
→ These two electrodes may be built into the same probe on use two separate probes.
(3) pH meter :
→ The principle of pH meter depends upon the exchange of ion from sample solution to the inner solution (pH 7 buffer ) of glass electrode thisrough the glugs membrane.
→ The porosity of the glass membrune decreases with the continuous use that decreases the perfor mance of the probe.
(4) Do Meter :
→ The Basic underlying the electrochemical determination of oxygen concentration is the use of membrane covered electro-chemical sensors.
→ If the anode is made of silver, the meter applied the required voltage.
3. Explain the working principle of ion selective meter, pH meter and Do meter and Electrodes.
• Ion-selective Meter :
→The ion selective electrode works based on principle of a galvanic cell.
- It consists of a reference electrode, ion selective membrane and voltmeter.
- The Transport of ions from an area of high concentrictions to low concentration through The selective binding of ions with of the membrane creates a the specific sites potential difference.
- The potential is measured with respect to a stable reference electrode having a constant potential of net change is determined.
- The difference in potential between the electrode & the membrane deped depends on the activity of the specific ion in solution.
- The strength of the net charge measured is directly proportional to the concentration of the selected son.
• PH Meter :
- A pH meter will be made up of a probe which itseIf is made up of two electrodes.
- This probe passes electrical signals to a meter.
- which displays the reading in pH units.
- The glass probs has two electrodes because one is Jalass sensor electrode f other is a reference electrode.
- Some pH meter do have separate probes in which case, one would be the sensor electrodes & the referce point.
- Both electrode are hollow bulbs a contain in a Ichloride solution with a silver chloride wire suspend into it.
- The glass sensing electrode has a bulb made upe of a vens special glass couted with silicca & metal salts.
- The glass sensing electrode measures the pit as the concentration of hydrogen ion surrounding the tip of thin walled glass bulb.
- Chemical potential between a known liquid inside the glass electrode fi unknown liquid outside.
- Because the thin glass bulb allows mainly the a angle & small hydrogen ion to intract with the glass.
- The glass electrode measures the electrochemical circuit also a reference electrode is needed.
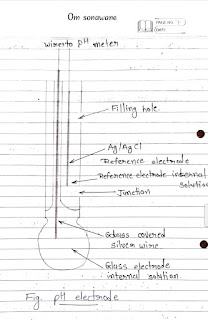
4. Along with meat sketch explain following electrodes.
• pH Electrode:
- The combination or pH electrode measures the difference in potentials between the two sides in the glass electrode
- To measure the potentials it must be a closed circuit.
- The circuit is closed through the internal solutions of the electrode and the external solution that is being measured & the pH meter.
- As the electrode is immersed in the test solution the
glass bulb senses the Htions as a millivolts (mu) due to the positive charge of the lit ions.
- The Electroly te or internal solution picks up mv
signal foom glass bulb.
- That signal is then passed to the internal electrode.
- The Ag/Ag cl wire than passes that signal to the electrod cable that leads to the metter.
- The circuit is closed by a minute amount of internal solution from the reference electrode flowing through la posous membrane made of a ceramic wick.
- This membrane or junction as it is called is located the electrode body.
• Ion- selective Electrode :
- Ion-selective electrode abo known as a specific ion electrode.
- It is a transduce or for that converts the activity
of a spefict specific ion dissolved in a solution into an electrical potential, which can be measured by a voltmeter.on pH meter.
- An ideal ion-selective electrode consists of a thin membrane gross which only the intended ion be transported.
- The transport of ions from a high conc. to a low. Lone through a selective binding with some sites within the membrane creates a potential difference.
- Ion selective electrodes work on the basic principle of the galvanic cell.
- By measuring the electric potential generated acroIss 4 membrane by "selected" ions, & comparing it to a reference electrode, a net charge determined.
- The strength of this charge is directly proportional to the concentration of the selected ions.
The basic formula is given for the galvanic cell.
| Ecell = EISE- Eref |
• Do Electrode
→ An inert metal such as gold on platinum anode and silver is use used for anode.
→ They are electrically connected with kcl or other electrolytic solution.
→ The complete cell is separated from sample by means of gas.
→ Permeable membrane usually made of polyethylene or Teflon.
→ When potential of about 0.5-0.8 v. is applied acro ss the anode & cathode any oxygen that passes
through the membrane will be reduced at cathode causing a current to flow.
→ The magnitude of current produced, is dissectly proportional to amount of Oxygen in sample.



.jpg)

0 Comments