1. Compare the Visual image Interpretation Digital Image processing
| Visual Image Interpretation |
Digital Image Processing |
| - It is a traditional approach based on human intuition and its success is experiment based. | - It is a Recent approach If Requires specialized Training. |
| - It is Time consuming. | - It is time effective - required much less time for interpretation. |
| - Very good for Extraction of spatial information. | - poor in extracting Spatial Information. |
| - Image Analyst is experience and knowledge is available. | - Image analyst's Experienced knowledge is not available result can be exactly Reproduced for any number of time. |
| - Interpretation Results may vary with time & person Depending upon Their Experieince & knowledge. | - It is complex, highly mathematical and Requires Expensive Equipments. |
- It Required Simple and inex-pensive equipment - The analysis poscess is subjective, quantitative & dependen't lon analyst based. |
- The process is obiective and Quantitative in in nature. |
2. Enlist & explain the key components of visual image Interpretation with example,
Tone:
→ Tone Refers to the colour or relative Brightness of an object in colour image f the relative & quantitati so shades of gray in black & white image.
→The Tonal variation is due to The Reflection, Transmittion or absorption Characteristics of an object This may vary from one object to another e from one band to another.
→It is one of the most basic Elements Because it is Difficult to Discean other Elements without Tonal difference.
→ It General, Smooth Surface Tends to have high Reflectance than gougher surface with less reflectance.
→In Thermal Imagenary Objets at Higher Temperature are Recorded in Highter tone compared to objects lat lower temperature, which appear of medium to darker tone.
→Similarly, top soil gives Dark tone compared to soil containg sand.
Shape :
→Shape Related to The General for your Configugation or outline of an individual object.
→Shape is one of The most important single Factors Recognising objects from images.
→Regular Geometric shapes are usually indicators of human presence of use.
→Similarly, Inregular shapes are usually indicators of natural objects.
→EX, A Railways line is usually Readily Distinguished from a Highway or an Unmetalled Road Because its shape consist of long Straight Tangents & gentle curves as opposed to the shape of Highway.
→The Shape of an object Viewed from above may be quite different from its profile view .
→For Planer objects, it is Easier to Calculates the gerial Dimensions on Imagery.
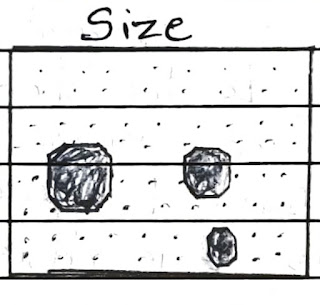
Size:
→Size of Objects in an image is a Function of Scal hence, The size of objects must be considered in the context of the scale of a photograph image Size of an object can be important tool for identification, in 2 ways.
→First, The size of Object or Feature is Relatively in Relation to other objects on the image.
→This is important Function of size, as it provide the interpretor with an interitivenation of scale Resolution of an image even though no measuren or calculations may have been made.
→This Role is achieved by Recognition of Familiar objects like dwelling Highways of Rivers.
→Second, absolute measurements can be e valuable as interpretation aid.
→We need to Remember the size of an object in an image depends on scale & resolution of an img.
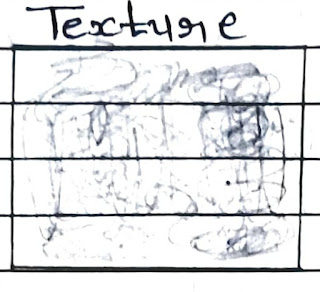
Texture
→ It is an Expression of Roughness or Smoothness las Exhibited by The images.
→ It is The Rate of Change of Tonal values
→ Texture signifies The Frequency of change & arrangement of Tones in an image & is Produced by an Aggregate of unit Features too small to be a clearly recognized individually on an image
→ Texture can be Expressed Qualitatively as coarse moderate, fine very fine, smooth, rough, rippled If mottle
→ Texture is depend upon tone, shape, size, pattern & scale of the imagenary & is produced by a mixture of features that are too small to be seen individually.
→ For Ex. Galassa & water generally appear ''smooth" while trees ar a forest Canopy may appear "Rough".
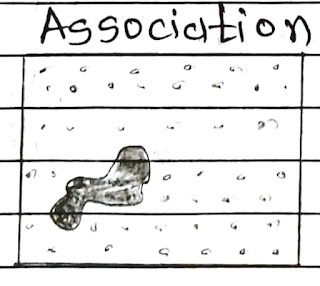
Association:
→ It is Occurence of Features in Relation to its Surroundings.
→ Some Times a single feature by if itself may not be distinctive enough by permit its dentification.
→ It species the occurence of certain objects on Features in association of a particular object or Features.
→ For Example: A primary school fo high school may be Similar flat Roofed Building structure but it may be possible to identify the high school by it association with an Adjected football field.
Shadow :
→ The outline or shape of a shadow provides a profile view of objects, which aids in image interpretation.
→ If the objects Within shadow Reflect Little light and are Difficult to Discean on image, which Hinders interpretation.
→ Military image interpreters are often primarily Pintrested in identifications of individual items Lof equipment.
→ Shadow is Significant in Distinguishing subtle Differences that might not be otherwise visible.
Site:
→ It Refers to The Topoggaphic position, for Example, sewage treatment facilities are positioned at low Topographic sites Near stream or Rivers to collect waste Flowing through the system from higher locations.
→ The Relationship of Feature to The Surrounding Features provides clup towards its identity. Identification of land forms can help in Deciphering the underlying geology.
→ Often many of The Rock Type have Distinct topography expression.
→ For Ex, some kinds of Sedimentary Rocks are Typically Exposed in form of alternating valley topography.
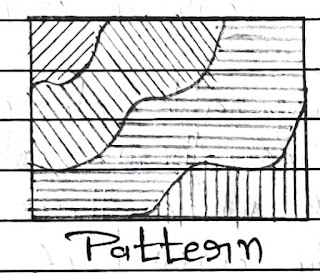
Pattern:
→ Pattern develops in an image due to spatial area.
→ Hence, pattern can be defined as the spatial aer angement of objects in an image.
→ Certain objects can be easily identified because of their pattern.
→ A particular pattern may have its genetic relation with several factors of its origin.
→ For ex, Urban & Rural Settlement Areas can be Easily identified based on the patterns created by the gaws of houses or buildings.
3. Compare the Thermal Properties of water & land.
→ Water has very dark to medium grey in day :
→ Thermal - IR images and moderately light Tones in night Thermal images compared with The Land.
→ This Response is due in part to a Rather High Thermal inertia relative to typical land surfaces, as controlled largely by waiter's high specific I heat.
→ Thus it Heats less During the Day & holds heat more at Night Giving rise under many Meteorological Conditions to Intrinsic cooler Daytime temperature & often warmer night time temperatures than most materials on land.
→ Also, being non-solid water in natural settings (Rivers, Lakes, Ocean's) is likely to experience disgyletion of its thermal gradient by convecting (upwelling) & Turbulence (Wave Action) that tends towards mixing & homogeneity, so that it's near surfa face temperatures vary by only a few degrees at most.
→ Water is the Responsible element in moist soils that tends to keep them cooler than drier soils.
→so that black & white thermal images show darker Spatterns where the mount of moisture is higher.
→The appearance in Thermal images of both water If land depends on the time of day.




.jpg)

0 Comments