1. Describe the camera system in Detail
→ Camera and their used for aerial photography are the simplest and oldest of sensor used for Remote Sensing of earth surface.
→ Camera are farming system which acquire near instantaneous "snapshot" of an area (A) of the surface camera system are positive optical sensor that use a lens (B) ( or systems of lens collectively referred to as to optics ) to from an image at focal plan (C) the plan at which an image are separately define.
2. Enlist List And Explain Types Of Camera.
→ Types of camera for aerial photography
- Matric camera
- Multi Lens camera
- large format camera
- panoramic camera
- strips camera
- panchromatic camera
(a) Matric Camera
→ A matric camera or arial mapping or single lens camera is one of which focal length and internal dimension are exactly know or can be determine through calibration.
Application :
→ production of digital orthophoto.
→ Preparation of plannematic and topographic maps.
→ Military intelligence such as targeting.
→ Finding distance angle size and shape of object.
Advantage :
→ Totally stable and precise camera.
→ principle distance is accurate know.
→lens with high Resolving power.
(b) Multi Lens Camera :
→ This camera has four lens and each of these lens consist different filter namely red green blue and infrared filter
→ Because of this reason it is term as multi lens or multispector or multiband camera.
Application :
→ Space based image
→ Environmental monitoring
→ Geo logical survey
→ Mapping natural and cultural resources
→ Military target tracking
→Farming
Advantage & Disadvantage
→ It has an advantage of ability to record reflective energy separately in district wavelength ranges.
→ This camera is now falling out of favour.
(C) Large Format Camera :
→ It is a camera with us Fame that measure 4'' - 5'' or more.
→ Due to 4''*5'' being the minimum requirement equipment maybe refracted to as a 4*5 camera.
Application :
→ used to record of history Christmas for the national park service documentation program.
→ Used in building survey landscape survey.
→ Was used in space shuttle for mapping and serving.
Advantage :
→ camera moments.
→ Incredible details and focus.
→ Highest quality footage and image around.
Disadvantage :
→ Unwieldy slow and heavy.
→ Composting via upside down image.
→ Expensive films and developing.
(d) Strip camera :
→ a shutterless camera in which the film most fast and exposing slit at a rate synchronized with that of the ground is know strip camera.
Uses :
→ Highly Determination.
→ Aircraft.
→ Railway Transportation.
→ Speed Measurement.
Advantages :
→ High Speed High pixel Deb and large image size.
→ Easy to configure options and other functionality.
Disadvantages :
→ no physical or protocol standards for interference with Fame grapes.
→ Required custom cables and connector.
→ Require camera films for using it with instruments image device.
(e) Panoramic camera :
→ it is a specialised equipment that capture image with horizontal fields or view.
→ And image showing a field of view equal or greater than that of human eye may be termed as panoramic camera.
Users :
→ it is a intent for low attitude use and used capturing and photo of around 180 degree of wide field.
→ It is used for this survey of dynamic resources were frequently coverage is required.
→It is also used for capturing astronomical images.
Advantages :
→ profitability.
→ Absence of blind sports and the effects of "seamless".
→ Multifunctionality.
Disadvantage :
→ high cost compared to convection network camera.
→ Need for a white communication channel.
(F) Panoramic camera :
→ the camera which form an image from panoramic data or capture a panoramic image or users panaromic films is term as panoramic camera.
Application :
→ it's finds application in forest and land cover survey and for greeting visual and near IR band data.
→Low geometric distance and can transfer be used for photogramatic purpose.
3. Enlist & Explain Types Of Filter.
- Absorption filter
- UV filter and skylight Filter
- interference Filter
- Anti-vignting Filter
- Polarizing filter
- Hass Filter
(A) Absorption Filter :
→ as name indicates this filter absorb and transmit energy of selected wavelength.
→ a yellow filter for example absorb blue energy includes upon its transmit green and red energy.
(b) Interference filter :
→ in interference filter is an optical filter that reflect one or more spectral band or lines and transmit other while monitoring a 0 coefficient of absorption or wavelength of interest.
→ Example the tin film of soap bubble which deflect spectrum of beautiful colour when illumination by natural/artificial light sources.
(c) Anti vignting filter :
→ It is an optical filter was density decrease radially for centre to compound radius decreasing illumination give by certain kinds of system particularly wide Angle lens system.
(d) Haze Filter :
→ Has filter has is caused by dust particle in air.
→ these particles reflect shortly wavelength more than longer once.
→ haze filter are designed to reduce hairs and one yellowish to counter exit to blue colour.
(e) UV and skylight filter :
→UV and Scarlet filter can also eliminate lake of sharpness caused by UV radiation and reduce distance haze.
→ UV filter are colourless and Skyline filters are pink lish both can effectively remove UV light.
(f) Polarizing filter :
→ polarizing filter often placed in front of camera lens in photography.
→ In order to darken skin manage reflectors aur supports glare for the surface of lekes.
4. Enlist & Explain Types Of Films.
- Infrared (B&W)
- panchromatic (B&W)
- colour film and
- colour IR
(a) Infrared (B&W) :
→ This film use sensitive entire 0.3 micrometre to 0.9 micrometer wavelength range and useful for detect difference in vegetation cover.
(b) panchromatic (B&W) :
→ This types of films produce black and white image and is most common types of films used for aerial photography.
→ The record image across routley the same spectral range as that of our eyes.
(c) Colours Film :
→ it's required most like then black and white films.
→ Since people can see more colour gradient they can in Grey toon colour photos typically allow greater interpreneurs of light with minor toner change.
(d) Colour IR :
→ It captures invisible I like from the red and of spectrum, lights that's not visible to ice and characteristically turning green we touch and bright red.
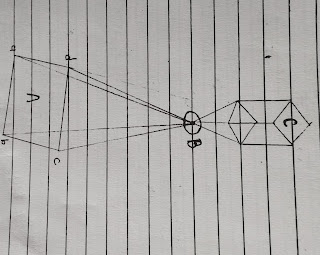
5. Explain the geometry of vertical aerial photography with diagram.
→ A photography image is central respective this implies that every light ray which reach the film surface during exposed Passed through camera lens.
→ Fig. Illustration basic geometric of VAP.
→ By vertical photography we mean and image taken with a camera that's is looking down at the ground.
→ As aircraft moves so does the camera this makes it impossible to take vertical image there force vertical image definition allow few degree diversion for nadir in summary.
→ A vertical image is an image that is either looking straight down to ground or is looking a few degree to either side of aircraft.
6. Define Following Terms :
(a) The Scale photography :
→ The scale photography HD ratio of distance on the image to corresponding distance on the ground also it is determine by focal length of camera and flying height above the ground.
→ also, it is determine by focal length of camera and flying height above the ground.
→ Mathematically,
→ Scale = F/H
Where,
f = focal length of camera.
H = flying height above ground level.
→ Scale of vertical photography is ratio of distance on photo to some distance on ground
S = F / ( H-h )
(b) Vantage point :
→ the term vantage point refer to position from which you take a photo.
→ Charging pure position changes the relationship between the background and your subject.
→ By changing your position multiple times during a shoot you can insure you get best result possible.
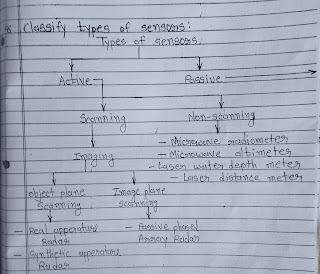
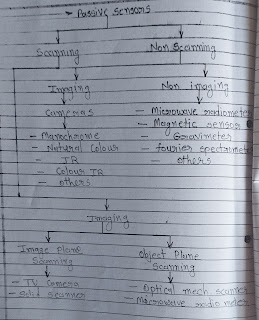
8. Classify Types Of Sensor.
→ There are two types of sensor active and passive.
→ Define the term black body discuss Stephan Bolt Mann low for TDS.
→ Black body is physical body that absorb the radiation that focus on it and emitted energy at Max possible rate per unit area at each wavelength for any given temperature.
Stephan Bolt Mann low :
→ It's States that : "the total energy radiation per unit area of black body in unit time is directly proportional to fourth power of black body temperature"
→ Mathematically,
M= o*T^4
Where,
M = total emitted tradition from black body ( W/m^4 )
O = Stephan Bolt Mann constant ( 5.6697 * 10^-8 )
T = temperature of amated body ( K or C° )
→ This low means the hotter the object the great amount of energy emitted corresponds to sum of integral of area under its curve.
9. Discuss Application Of Thermal Image.
→ Thermal image originally develop for military use during the Korean war the thermal image camera have magnitude into other fields and have found many uses.
→ Firefighter use them to see through smoke find people and localised hotspot of fire.
→ Low enforcement uses to manage surveillance activities located and apprehend suspect investigate crime sciences and conduct search and operation.
→ Power line maintenance technique located overheating joints and part 2 eliminate potential failures.
→ Where thermal insulation become faulty.
→ building construction technique can see heat lips to improve efficiency of cooling or heating.
→ Physiological activity such as Fiverr in human beings and over warm bloody animals can also be monitored with thermographic image.
→ They are also used commonly in hydrology.



.jpg)

0 Comments